Difference between revisions of "Poisson's ratio"
(Created page with "Poisson ratio is one of the important criteria to be considered in pipe selection where the system may be subjected to sub-atmospheric pressure (e.g. Siphonic drainage syste...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Poisson ratio is one of the important criteria to be considered in pipe selection where the system may be subjected to sub-atmospheric pressure (e.g. [[Siphonic drainage systems]]). In general, a lower value in Poisson ratio provides better strength against collapse of pipe due to sub-atmospheric pressure. | Poisson ratio is one of the important criteria to be considered in pipe selection where the system may be subjected to sub-atmospheric pressure (e.g. [[Siphonic drainage systems]]). In general, a lower value in Poisson ratio provides better strength against collapse of pipe due to sub-atmospheric pressure. | ||
| − | In evaluating the limiting or maximum pressures, forces and deflections on plastic pipe, fittings and components covered by this standard, the material properties listed in Table 8.1 are assumed at an operating temperature of 20°C (68°F). | + | In evaluating the limiting or maximum pressures, forces and deflections on plastic pipe, fittings and components covered by this standard, the material properties listed in Table 8.1 are assumed at an operating temperature of 20°C (68°F).<ref> ASPE Standard 45 </ref> |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | !colspan="6"|Table 8.1: Material Properties at an Operating Temperature of 20°C (68°F) | + | !colspan="6"|Table 8.1:Material Properties at an Operating Temperature of 20°C (68°F) |
|- | |- | ||
| + | |'''Property/ Material''' | ||
| + | |'''Tensile Modulus of Elasticity''' | ||
| + | |'''Creep Modulus''' | ||
| + | |'''Poisson’s Ratio''' | ||
| + | |'''Rate of Thermal Expansion''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Symbol | ||
| + | |<math>E_t</math> | ||
| + | |<math>E_c</math> | ||
| + | |<math>\mu</math> | ||
| + | |<math>C_{tx}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Units | ||
| + | |Mpa(psi) | ||
| + | |Mpa(psi) | ||
| + | |dimensionless | ||
| + | |cm/cm/°C (ft/ft/°F) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ABS | ||
| + | |2,206 (320,000) | ||
| + | |rowspan="2"|Varies (refer to 8.2.2) | ||
| + | |0.35 | ||
| + | |10.3 E-5 (5.7 E-5) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |HPDE | ||
| + | |862 (125,000) | ||
| + | |0.45 | ||
| + | |18.0 E-5 (10.0 E-5) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PVC | ||
| + | |2,827 (410,000) | ||
| + | |0.35 | ||
| + | |5.2 E-5 (3.0 E-5) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Test Method | ||
| + | |ASTM D638 | ||
| + | |ISO 899 | ||
| + | |ASTM E132 | ||
| + | |ASTM D696 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Calculation of allowable pressure <math>(Pa)</math>: The minimum required pipe wall thickness <math>(t)</math> shall be based on Equations 8.1 and 8.2 in Table 8.2 and the mechanical and dimensional properties of the pipe material evaluated. Equations 8.1 and 8.2 apply for a long cyclindrical tube of length L and wall thickness t under uniform external pressure with (R/t) > 10.<ref> ASPE Standard 45 Cl.8.3.9 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | !colspan="6"|Table 8.2 Pipe Wall Thickness Calculations | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Equation 8.1 When <math> L \ge 4.9R \sqrt{\frac{R}{t}}</math> | ||
| + | |Equation 8.2 When <math> L \le 4.9R \sqrt{\frac{R}{t}}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<math>P_{cr}= \frac{E_c}{3(1-\mu^2)} \Big[ \frac{t}{R} \Big]^3</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | == References == | ||
Revision as of 11:25, 3 October 2017
Poisson ratio is one of the important criteria to be considered in pipe selection where the system may be subjected to sub-atmospheric pressure (e.g. Siphonic drainage systems). In general, a lower value in Poisson ratio provides better strength against collapse of pipe due to sub-atmospheric pressure.
In evaluating the limiting or maximum pressures, forces and deflections on plastic pipe, fittings and components covered by this standard, the material properties listed in Table 8.1 are assumed at an operating temperature of 20°C (68°F).[1]
| Table 8.1:Material Properties at an Operating Temperature of 20°C (68°F) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Property/ Material | Tensile Modulus of Elasticity | Creep Modulus | Poisson’s Ratio | Rate of Thermal Expansion | |
| Symbol | 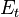
|
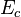
|
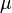
|
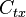
| |
| Units | Mpa(psi) | Mpa(psi) | dimensionless | cm/cm/°C (ft/ft/°F) | |
| ABS | 2,206 (320,000) | Varies (refer to 8.2.2) | 0.35 | 10.3 E-5 (5.7 E-5) | |
| HPDE | 862 (125,000) | 0.45 | 18.0 E-5 (10.0 E-5) | ||
| PVC | 2,827 (410,000) | 0.35 | 5.2 E-5 (3.0 E-5) | ||
| Test Method | ASTM D638 | ISO 899 | ASTM E132 | ASTM D696 | |
Calculation of allowable pressure 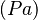 : The minimum required pipe wall thickness
: The minimum required pipe wall thickness 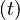 shall be based on Equations 8.1 and 8.2 in Table 8.2 and the mechanical and dimensional properties of the pipe material evaluated. Equations 8.1 and 8.2 apply for a long cyclindrical tube of length L and wall thickness t under uniform external pressure with (R/t) > 10.[2]
shall be based on Equations 8.1 and 8.2 in Table 8.2 and the mechanical and dimensional properties of the pipe material evaluated. Equations 8.1 and 8.2 apply for a long cyclindrical tube of length L and wall thickness t under uniform external pressure with (R/t) > 10.[2]
| Table 8.2 Pipe Wall Thickness Calculations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Equation 8.1 When 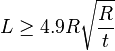
|
Equation 8.2 When 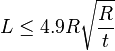
| ||||
![P_{cr}= \frac{E_c}{3(1-\mu^2)} \Big[ \frac{t}{R} \Big]^3](/images/math/2/9/a/29ab972ed6ad2a230a9e04a159c3ee64.png)
| |||||