Difference between revisions of "Colebrook-White Equation"
(Created page with "[1] The governing equation used to calculate the expected friction loss factor (f) used in the Darcy-Weisbach Equation. The equation is a function of pipe surface roughness, p...") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | * The governing equation used to calculate the expected friction loss factor (f) used in the Darcy-Weisbach Equation. The equation is a function of pipe surface roughness, pipe diameter, fluid viscosity and fluid velocity. | |
| − | + | * The loss of energy head, <math>\Delta h_F</math>, due to wall friction in a length of pipe between points 1 and 2 in a system is given by: | |
<math>\Delta h_F = i_FL_p</math> <br clear = all> | <math>\Delta h_F = i_FL_p</math> <br clear = all> | ||
The frictional head loss gradient, <math>i_F</math>, can be determined from the '''Colebrook-White equation''', which for pipes flowing 100% full of water may be written in the form; | The frictional head loss gradient, <math>i_F</math>, can be determined from the '''Colebrook-White equation''', which for pipes flowing 100% full of water may be written in the form; | ||
| − | <math>i_F = ( \frac{u^2}{8gd_1} ) | + | <math>i_F = ( \frac{u^2}{8gd_1} ) { \Big\{ {log_{10}} [ \frac{k_p}{3710d_1} + \frac{1.775v} {\sqrt{(gi_F {d_i}^3})} ]} \Big\}^{-2}</math> |
| − | |||
| − | NOTE: An iterative method of solution is required to find the head loss gradient, | + | NOTE: An iterative method of solution is required to find the head loss gradient, <math>i_F</math>, from equation above because this quantity also appears on the right-hand side of the equation. |
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | # ASPE Standard 45 Siphonic Roof Drainage 2007 | ||
| + | # BS EN 8490:2007 Guide to siphonic roof drainage systems | ||
Latest revision as of 09:57, 12 September 2017
- The governing equation used to calculate the expected friction loss factor (f) used in the Darcy-Weisbach Equation. The equation is a function of pipe surface roughness, pipe diameter, fluid viscosity and fluid velocity.
- The loss of energy head,
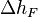 , due to wall friction in a length of pipe between points 1 and 2 in a system is given by:
, due to wall friction in a length of pipe between points 1 and 2 in a system is given by:
The frictional head loss gradient, 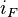 , can be determined from the Colebrook-White equation, which for pipes flowing 100% full of water may be written in the form;
, can be determined from the Colebrook-White equation, which for pipes flowing 100% full of water may be written in the form;
NOTE: An iterative method of solution is required to find the head loss gradient,, from equation above because this quantity also appears on the right-hand side of the equation.
References
- ASPE Standard 45 Siphonic Roof Drainage 2007
- BS EN 8490:2007 Guide to siphonic roof drainage systems
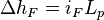
![i_F = ( \frac{u^2}{8gd_1} ) { \Big\{ {log_{10}} [ \frac{k_p}{3710d_1} + \frac{1.775v} {\sqrt{(gi_F {d_i}^3})} ]} \Big\}^{-2}](/images/math/f/5/b/f5bd8dd0443c912e9b2e6c4a2076d721.png)