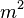Difference between revisions of "Catchment area (effective) (roof drainage)"
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
Where two or more walls from an angle or bay, the direction of the wind should be assumed to be such that the walls considered together present the maximum vertical area to the rain, as illustrated in Figure below; | Where two or more walls from an angle or bay, the direction of the wind should be assumed to be such that the walls considered together present the maximum vertical area to the rain, as illustrated in Figure below; | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Catchment-Area-Effective-Vertical-Surfaces.jpeg]] |
For an enclosed area, the effective catchment area will be its plan area unless the surrounding walls are of unequal height. In the latter case, the value of A should be increased by half the area in the elevation by which the higher wall exceeds the lower wall. | For an enclosed area, the effective catchment area will be its plan area unless the surrounding walls are of unequal height. In the latter case, the value of A should be increased by half the area in the elevation by which the higher wall exceeds the lower wall. | ||
Revision as of 15:21, 11 April 2017
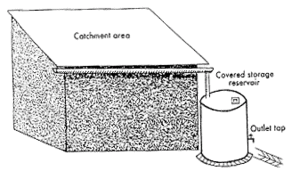
- Area to be drained within a roof. Unit of measurement is in square meter
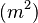 .
.
- Catchment area can be a flat or sloping roof/ surfaces and also includes vertical surfaces.
- Effective catchment area for vertical surfaces
Single wall shall be 50% of its total surface area up to a maximum exposed height of 33feet (10metres).
- Effective Catchment Area
- Flat roofs
- Sloping roofs The effective area, A, roof draining to an eaves or parapet gutter (should be calculated using the table below)
| Effective Impermeable Roof Area | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allowance to be made for the effect of wind | Effective impermeable roof are, A
| ||||
| Wind driven rain, 26degrees to vertical | 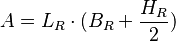
| ||||
| Rain perpendicular to roof(i.e. surface area of roof used) | 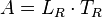
| ||||
NOTES:
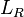 is the length of roof to be drained, in metres (m);
is the length of roof to be drained, in metres (m);
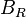 is the plan width of roof from gutter to ridge, in metres (m);
is the plan width of roof from gutter to ridge, in metres (m);
 is the height of roof from gutter to ridge, inmetres (m);
is the height of roof from gutter to ridge, inmetres (m);
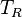 is the distance from gutter to ridge measured along the roof, in metres (m);
is the distance from gutter to ridge measured along the roof, in metres (m);
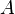 is the effective impermeable roof area, in square metres
is the effective impermeable roof area, in square metres 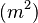
Figure below illustrated these dimensions.
- For valley gutter, one side of the roof will tend to be exposed to the wind and the other will tend to be sheltered. The methos of calculating the effective catchment are illutrated on the Figure below;
Run off from any vertical wall should be added to the effective catchment area.
In area where wind is taken into account in rainfall calculations, where rain driven against a wall by the wind is taken;
Vertical surfaces The effective catchment area of a single wall should be taken as 50% of its area, up to a maximum height of 10 meters. Where two or more walls from an angle or bay, the direction of the wind should be assumed to be such that the walls considered together present the maximum vertical area to the rain, as illustrated in Figure below;
For an enclosed area, the effective catchment area will be its plan area unless the surrounding walls are of unequal height. In the latter case, the value of A should be increased by half the area in the elevation by which the higher wall exceeds the lower wall.
Small Roofs For small roof area not exceeding 6 sq.mts. and no other area drains onto it, gutters and rainwater pipes may be omitted from a roof at any height.
Tall buildings Gutters and rainwater pipes may be omitted from tall structures where runoff would be dispersed before the ground. Such runoff should be directed so as to avoid undesirable pattern staining and splashing of windows.
References:
- BS EN 12056-3
- SS 525:2006 Code of Practice for Drainage of roofs
- ASTM A112.6.9 Standard for Siphonic Roof drainage Systems