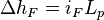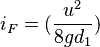Difference between revisions of "Colebrook-White Equation"
(Created page with "[1] The governing equation used to calculate the expected friction loss factor (f) used in the Darcy-Weisbach Equation. The equation is a function of pipe surface roughness, p...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 15:59, 8 September 2017
[1] The governing equation used to calculate the expected friction loss factor (f) used in the Darcy-Weisbach Equation. The equation is a function of pipe surface roughness, pipe diameter, fluid viscosity and fluid velocity.
[2] The loss of energy head, 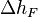 , due to wall friction in a length of pipe between points 1 and 2 in a system is given by:
, due to wall friction in a length of pipe between points 1 and 2 in a system is given by:
The frictional head loss gradient, 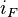 , can be determined from the Colebrook-White equation, which for pipes flowing 100% full of water may be written in the form;
, can be determined from the Colebrook-White equation, which for pipes flowing 100% full of water may be written in the form;
i_"F " =(u^2/(8gd_1 )) {log_10[k_p/(3710d_1 )+1.775"v" /√(gi_"F" d_i^( 3) )] }^(-2)
NOTE: An iterative method of solution is required to find the head loss gradient, i_"F " , from equation because this quantity also appears on the right-hand side of the equation.