Absolute Pressure
There are many ways to measure pressure and 2 of the most common are using gauge pressure and absolute pressure. They give different reading to the same pressure value. This is due to their different reference point.
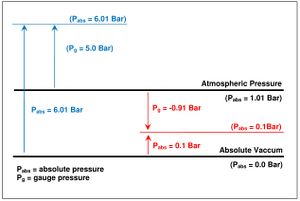
Absolute pressure is measured relative to the absolute zero pressure - the pressure that would occur at absolute vacuum. When absolute pressure = zero, means it is prefect vacuum. Absolute pressure can only have a positive value
Gauge pressure is measured relative to atmospheric pressure. When gauge pressure = zero means it is atmospheric pressure. When it is a positive reading measure the pressure is higher than the atmosphere pressure, when it’s a negative value it means the pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure, sometimes this is referred as vacuum pressure.
The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is about 1.01 bar. However atmospheric can change due temperature and elevation. The higher you are the lower is the atmospheric pressure.
Hence for absolute pressure reading of 0.1 bar translate to gauge pressure reading of -0.91 bar and conversely a gauge pressure reading of 5.0 bar translate to absolute pressure reading of 6.01 bar.